Please note that this article was orginally written in June 2013.
In April 2014, the Singapore NEA has updated the PSI calculation to also include PM2.5. http://www.nea.gov.sg/anti-pollution-radiation-protection/air-pollution-control/psi
In April 2014, the Singapore NEA has updated the PSI calculation to also include PM2.5. http://www.nea.gov.sg/anti-pollution-radiation-protection/air-pollution-control/psi
最近來自印尼的東南亞霧霾影響了新加坡和現在的馬來西亞,我們有很多疑問,為什麼新加坡國家環境局網站( nea.gov.sg )和新加坡世界空氣品質指數項目的數據存在差異?網頁。
例如,今天可以在 NEA 網站上看到以下內容:

由於某些歷史原因,新加坡使用PSI (污染物標準指數)來評估空氣品質。在上圖中,數字 1 對應於用於 PSI 評估的 PM10 值。值67(/59)可讀取為 67 µg/m3,對應於 PSI 59。PSI 被評估為每種污染物的單一 PSI 的最大值:PM 10 、SO 2 、NO 2 、O 3 (臭氧)和CO 2 。
PSI(Singapore-North) = max( PSIPM10-based, ... PSIO3-based )= max (59, ..., 77) = 77
儘管如此,有趣的是,在同一個表中,最後一列也提供了 PM2.5 資料(參見圖 3)。該數據僅以 μg/m3 為單位提供(參見 2),並且沒有轉換為 PSI 之類的數據(即從 PM2.5 質量轉換為污染或質量指數)。然而,這種轉換是存在的,並且是由美國環保署定義的。進行轉換的最簡單方法是使用線上計算器,可在airnow.gov上找到:
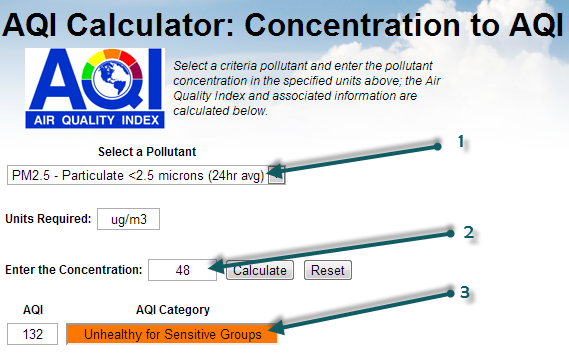
If you select the PM2.5 (1), then enter the mass concentration of 48 (2), can click on Calculate, you will obtain the AQI of 132 (3). So, based on the PM2.5 AQI conversion, the PSI that is used for Singapore could be extended (let's call it PSI++) to also take into account the PM2.5 information. In which case, the PSI++ would be the maximum of the regular PSI (based on PM10 only) and the PM2.5 AQI:
PSI++ = max( PSI, AQIPM.25 ) = max( 77, 132 ) = 132
This PSI++, that is commonly referred as AQI (or Air Quality Index), is what is being used on the the World Air Quality Index project, for all the cities (provided PM2.5 is available for the city). And this explains why the values are different between the NEA website and the World Air Quality Index project.
Note: With the PSI update from April 2014, the only remaining difference is that the World Air Quality Index project is using a 1-hour PM2.5 reading (following the instantcast) while Singpore PSI is based on the 3 hours average.
Moreover, when doing the convertion, make sure you use the 1-hour reading for the PM2.5 concentration rather than the 24-hours averaged value, as shown on the below image:
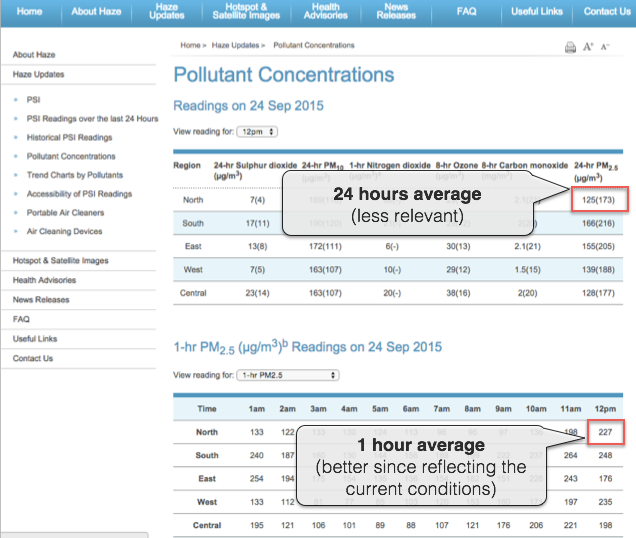
http://www.haze.gov.sg/haze-updates/pollutant-concentrations/type/PM25-1Hr
Moreover, when doing the convertion, make sure you use the 1-hour reading for the PM2.5 concentration rather than the 24-hours averaged value, as shown on the below image:

http://www.haze.gov.sg/haze-updates/pollutant-concentrations/type/PM25-1Hr
If you want to know more about PM10 vs PM2.5, and especially why PM10 is still used, please check the faq entry about why is PM2.5 often higher than PM10? Is PM10 still a relevant measure?
--
Note: This article is part of a series on Worldwide Air Quality scales.
For more information about specific countries or continent, please refer to those articles: Thailand and Malysia - India - China - Hong Kong / Canada (Air Quality Health Index) - South America - Australia - Quebec and Montreal - Singapore - Poland - Indonesia .
For more information about specific countries or continent, please refer to those articles: Thailand and Malysia - India - China - Hong Kong / Canada (Air Quality Health Index) - South America - Australia - Quebec and Montreal - Singapore - Poland - Indonesia .
For information about the 24 hours averaging used or Ozone and Particulate Matter (PM2.5), please refer to those two articles: Ground Ozone Index - PM2.5 Instant Cast
